Stingless bee hive design is crucial for sustainable agriculture, offering eco-friendly solutions․ These hives support biodiversity and pollination, aligning with modern environmental goals, while ensuring efficient honey production․
Overview of Stingless Bee Hive Design
Stingless bee hive design combines traditional and modern techniques to create habitats for these beneficial pollinators․ Hives are crafted from natural materials like wood and bamboo, or innovative synthetics, ensuring durability and adaptability․ Designs range from natural logs to modular boxes, tailored for various climates and bee species․ The goal is to mimic natural nesting sites, promoting colony health and honey production․ These hives are essential for conservation, pollination, and sustainable agriculture, offering a harmonious blend of functionality and environmental stewardship․
Importance of Stingless Bee Hive Design
Stingless bee hive design is vital for promoting pollination, enhancing biodiversity, and supporting sustainable agriculture․ It ensures the health of colonies, contributing to ecological balance and honey production․
Role in Meliponiculture
Meliponiculture, the practice of stingless beekeeping, relies heavily on well-designed hives to support colony health and productivity․ Proper hive structures ensure optimal conditions for brood development, honey storage, and colony growth․ They also facilitate easier monitoring and maintenance, crucial for sustainable beekeeping․ Effective hive designs promote the conservation of stingless bees while enabling the harvesting of valuable products like honey and propolis․ This practice not only supports biodiversity but also provides economic opportunities for local communities, making it a vital component of sustainable agriculture and environmental stewardship․
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Stingless bee hive designs promote environmental sustainability by supporting pollination and biodiversity․ They help reduce deforestation by providing alternatives to harvesting wild colonies․ Economically, these hives enable the production of valuable products like honey, beeswax, and propolis, supporting local livelihoods․ Sustainable hive practices also encourage eco-friendly agriculture and community involvement, fostering both ecological conservation and economic growth․ This dual benefit makes stingless beekeeping a vital practice for environmental stewardship and economic development worldwide․

Key Characteristics of Stingless Bees
Stingless bees are social insects, living in colonies with a queen, workers, and brood․ They are non-aggressive, ideal for urban environments, and play a crucial role in pollination․
Biology and Behavior
Stingless bees are highly social creatures, thriving in structured colonies with a queen, thousands of workers, and brood cells․ Workers gather pollen and nectar, utilizing plant resins to construct hives․ Their colonies are known for intricate communication and division of labor․ Unlike honeybees, they are non-aggressive, making them ideal for urban settings․ Their behavior is centered around hive maintenance, resource collection, and reproduction, ensuring colony survival and productivity․
Differences from Honeybees
Stingless bees differ significantly from honeybees in several aspects․ They are non-aggressive and do not sting, making them safer for urban environments․ Their honey production is minimal compared to honeybees, yielding less than one kilogram annually․ Additionally, stingless bees construct unique spiral hives, often using resin and wax, which are distinct from honeybees’ vertical combs․ Their colony structure and behavior are also more specialized, focusing on specific nesting sites and resource gathering methods․ These differences highlight their unique role in pollination and ecosystem health․
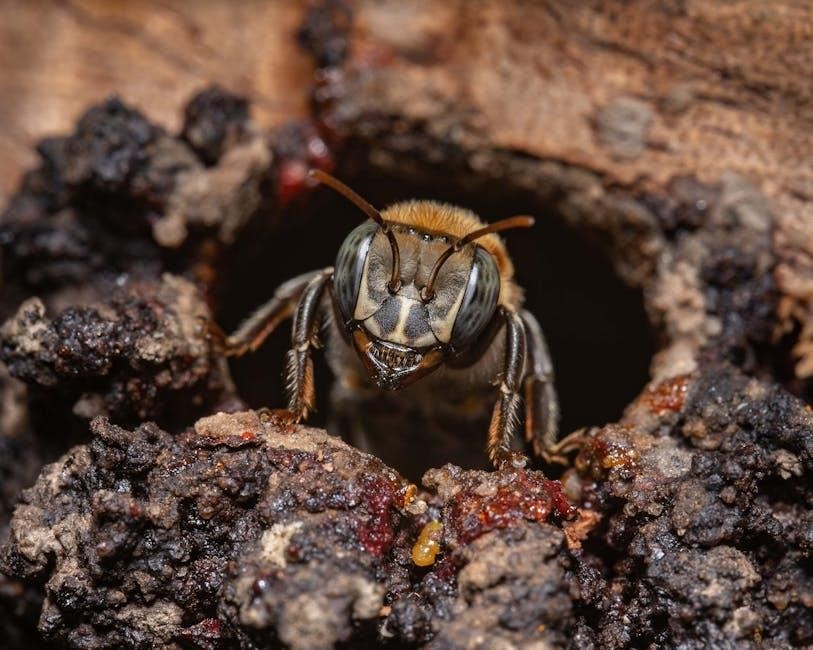

Materials Used in Hive Construction
Stingless bee hives often use natural materials like bamboo, logs, and resin, while modern designs incorporate PVC and 3D-printed components for durability and sustainability․
Natural Materials
Natural materials like bamboo, logs, and plant resins are widely used in stingless bee hive construction․ Bamboo hives are durable and eco-friendly, while logs mimic the bees’ natural nesting sites; Resin, collected by stingless bees, is used to construct internal structures and seal hives, enhancing protection․ These materials align with the bees’ natural habitat preferences, promoting colony health․ They also support biodiversity and are cost-effective, making them ideal for sustainable meliponiculture practices․ Natural materials ensure a harmonious integration of hives into ecosystems, fostering environmental balance and bee conservation․
Modern Materials
Modern materials like PET-G, PVC, and 3D-printed components are increasingly used in stingless bee hive design․ These materials provide durability and climate adaptability, offering better protection for colonies․ PET-G and PVC are lightweight, easy to clean, and resistant to pests and diseases․ 3D printing allows for customized hive structures, enhancing space efficiency and colony comfort․ These innovative materials combine functionality with sustainability, supporting the growth of stingless bee populations in diverse environments while maintaining ecological balance and promoting efficient meliponiculture practices globally․
Recycled Materials
Recycled materials, such as reclaimed wood, bamboo, and repurposed plastic, are gaining popularity in stingless bee hive construction․ These eco-friendly options reduce environmental impact while maintaining durability․ Recycled wood retains natural insulation properties, benefiting colony health․ Bamboo, lightweight and renewable, is ideal for portable hives․ Repurposed plastic, like PVC, offers pest resistance and ease of cleaning․ Using recycled materials aligns with sustainability goals, supports conservation efforts, and promotes meliponiculture practices that prioritize environmental stewardship․ This approach ensures hives are both functional and environmentally responsible, meeting the needs of modern beekeeping while preserving natural resources․
Design Considerations
Stingless bee hive design must prioritize climate adaptability, space efficiency, and ease of maintenance․ These factors ensure optimal colony health and productivity while minimizing environmental impact․
Climate Adaptability
Stingless bee hive design must emphasize climate adaptability to ensure the survival and productivity of colonies in diverse environments․ Hive structures are crafted to suit various climates, from tropical to temperate regions, using materials like PET-G and PVC for durability and thermal regulation․ For instance, the Temperate Climate (TC) hive mimics natural nesting sites found in cooler areas, enhancing colony resilience․ Such designs not only support pollination but also contribute to biodiversity conservation and sustainable agriculture practices․
Space Efficiency
Space efficiency is a critical factor in stingless bee hive design, particularly for urban environments․ Compact hive structures like the INPA square modular box maximize limited space while maintaining colony health․ These designs allow for efficient honeycomb organization, ensuring adequate storage of honey and pollen․ Modern materials and modular systems enable easy expansion, making them suitable for both small gardens and larger agricultural settings․ This approach promotes sustainable beekeeping without compromising on productivity or colony well-being․

Ease of Maintenance
Ease of maintenance is a key consideration in stingless bee hive design, ensuring optimal colony health and productivity․ Modular components, such as removable frames and drawers, simplify inspections and honey harvesting․ Designs like the ASB dry split box and INPA modular systems allow for easy access, reducing disruption to the colony․ Smooth surfaces and streamlined structures also facilitate cleaning and pest control․ These features make hive maintenance manageable for both experienced beekeepers and newcomers, promoting sustainable and efficient meliponiculture practices․
Types of Stingless Bee Hives
Natural hives, bamboo hives, log artificial hives, and temperate climate designs are common types, each offering unique benefits tailored to specific climates and bee species needs․
Natural Hives
Natural hives mimic the bees’ original nesting sites, often found in tree cavities․ They are typically hollow logs or tree holes, providing a sheltered environment․ These hives require minimal intervention, promoting colony health and natural behavior․ Their design emphasizes sustainability, preserving the bees’ instinctive habits․ Natural hives are ideal for conservation efforts, as they closely replicate the bees’ wild habitat, ensuring a thriving ecosystem․ This approach supports biodiversity and reduces environmental impact, making them a popular choice for eco-conscious beekeepers․
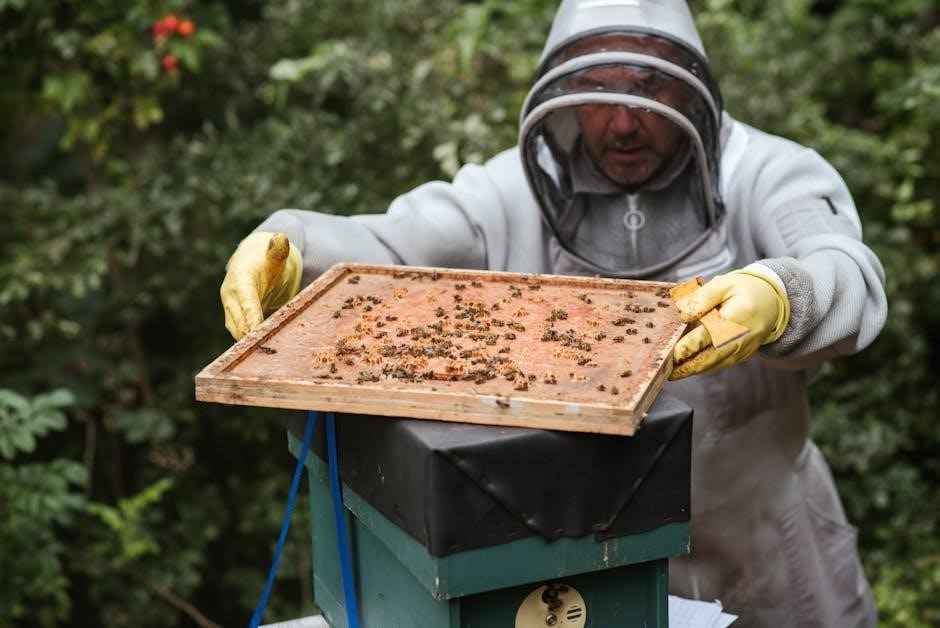

Bamboo Hives
Bamboo hives offer a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative for stingless beekeeping․ Bamboo’s natural durability and resistance to pests make it an ideal material․ These hives are often designed to mimic the bees’ natural nesting habits, providing a familiar environment․ Bamboo hives are lightweight, easy to transport, and can be tailored to specific climate conditions․ They are particularly popular in regions where bamboo is abundant, promoting local materials and reducing costs․ This design supports both the bees and the environment, making it a favored choice for small-scale beekeepers․
Log Artificial Hives
Log Artificial Hives (LAHs) are a popular choice for stingless beekeeping, designed to mimic natural nesting sites․ They are often constructed from hollowed logs, providing a familiar environment for the bees․ LAHs are particularly effective in regions like Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland, where they have been successfully used to domicile colonies․ This design supports colony establishment and is favored for its simplicity and environmental suitability․ LAHs are also lightweight and easy to maintain, making them ideal for small-scale beekeeping operations and conservation efforts․
Temperate Climate Hive Design
Temperate Climate Hives (TCHs) are engineered to replicate natural nesting environments found in cooler regions․ These designs emphasize insulation and adaptability, ensuring colony survival in fluctuating temperatures․ TCHs often feature adjustable entrances and internal compartments for honey storage and brood rearing․ Their construction prioritizes materials like wood or insulated plastics to maintain stable internal conditions․ This design has proven effective in enhancing colony resilience and honey production in temperate zones, making it a valuable option for beekeepers in regions with distinct seasonal changes․
Construction Plans and Blueprints
Standard OATH, INPA modular, and ASB dry split box designs provide detailed blueprints for constructing stingless bee hives, ensuring colony health and honey production efficiency in various climates․
Standard OATH Box Design
The Standard OATH box design is a popular choice for stingless beekeeping, offering simplicity and effectiveness․ Its structure includes an entrance hole for easy access, internal compartments to mimic natural nesting sites, and materials like wood or recycled plastics for durability․ This design supports colony health by maintaining optimal temperature and humidity, crucial for honey production․ The OATH box is widely used in programs like the Ku-ring-gai Native Stingless Bee Program, promoting sustainable beekeeping practices globally․ Its modular nature allows for easy expansion, making it ideal for both hobbyists and commercial use․
INPA Square Modular Box Plans
The INPA Square Modular Box is a versatile design for stingless beekeeping, offering a structured environment for colony growth․ Plans include A4 and A3 printing options for precise construction․ The box features a modular layout, allowing easy expansion and maintenance․ Its design supports optimal temperature and humidity control, essential for colony health․ The INPA box is praised for its scalability, making it suitable for both small-scale hobbyists and large-scale beekeeping operations․ This design is widely adopted due to its practicality and ease of use for beekeepers of all levels․
ASB Dry Split Box Design
The ASB Dry Split Box Design is a practical and efficient hive system for stingless beekeeping․ It features a split-box structure, allowing easy access for inspections and honey harvesting․ The design emphasizes dry conditions, reducing moisture-related issues․ Ideal for Australian native bees, it supports colony health and productivity․ Its simplicity makes it accessible for beekeepers of all experience levels, while its durability ensures long-term use․ This design is particularly favored for its ease of maintenance and adaptability to various environmental conditions․
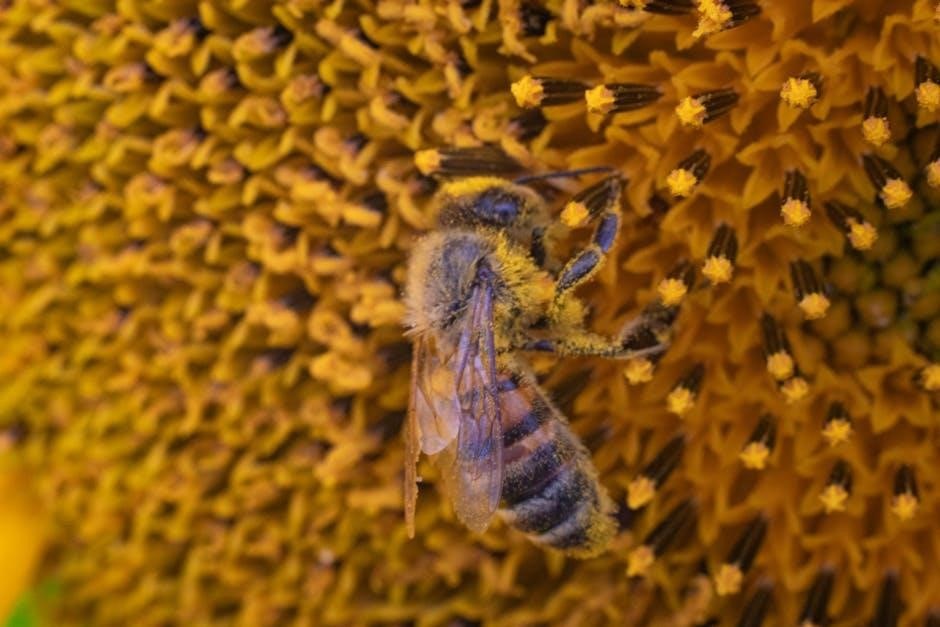

Economic Importance of Stingless Bees
Stingless bees contribute significantly to economies through honey, beeswax, and pollination services, supporting sustainable agriculture and local industries while promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health globally․
Honey Production
Stingless bees produce high-quality honey in smaller quantities compared to honeybees, with unique flavors and medicinal properties․ Proper hive designs, like the ASB dry split box and INPA square modular box, enhance honey production by providing controlled environments․ These designs ensure efficient extraction while preserving the honey’s natural qualities․ The honey, often described as having a distinctive bush taste, is highly valued for its culinary and health benefits, making it a sought-after product in local and niche markets globally․
Beeswax and Propolis Utilization
Stingless bees collect plant resins and wax to construct pots for storing honey and bee bread․ Hive designs like the INPA square modular box provide spaces for these pots, enhancing efficiency․ Beeswax and propolis are valued for cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, boosting their economic importance․ Proper hive structures support natural resin collection, ensuring high-quality products․ This sustainable practice aligns with environmental conservation, making stingless beekeeping a valuable agricultural activity․
pollination Services
Stingless bees play a vital role in pollination, enhancing biodiversity and crop productivity․ Their activity supports local ecosystems and agriculture, making them invaluable for environmental sustainability․ Hive designs like the Temperate Climate Hive optimize their pollination efficiency, ensuring robust ecological support․ These bees are particularly effective in urban gardens and natural habitats, contributing to food security and ecosystem health․ Their pollination services are indispensable for maintaining balanced ecosystems and promoting agricultural prosperity․

Conservation Efforts
Stingless bee conservation programs focus on protecting natural habitats and promoting sustainable hive designs, ensuring biodiversity and reducing deforestation through community-driven initiatives and education․
Domestication Programs
Domestication programs for stingless bees focus on creating sustainable hive systems to protect these pollinators․ Initiatives like the Ku-ring-gai Native Stingless Bee Program and Cumberland City Council’s project promote hive designs that mimic natural habitats, encouraging colony health․ These programs often involve community education, hive distribution, and research collaborations to adapt hives for various climates․ By supporting domestication, these efforts help conserve stingless bee populations, reduce deforestation, and foster eco-friendly agriculture, ensuring biodiversity and ecological balance for future generations․
Community Involvement
Community involvement is a cornerstone of stingless bee conservation and hive design initiatives․ Programs like the Ku-ring-gai Native Stingless Bee Program and Cumberland City Council’s Keepin-A-Hive initiative engage residents in hive management and pollination efforts․ These programs often include workshops, training sessions, and the distribution of hive components, fostering a sense of ownership and environmental stewardship․ By involving local communities, these initiatives not only promote biodiversity but also empower individuals to contribute to sustainable agriculture and ecosystem health, ensuring the long-term survival of stingless bees․
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Legal and ethical considerations in stingless bee hive design involve ensuring compliance with local regulations and promoting sustainable practices․ Conservation efforts must align with environmental laws, while ethical practices focus on minimizing harm to colonies and ecosystems․ Programs like the Ku-ring-gai Native Stingless Bee Program emphasize responsible hive management, balancing human activity with ecological preservation․ Ethical guidelines also address the use of materials and techniques that support biodiversity and pollination services without exploiting natural resources․
Community and Educational Programs
Community initiatives like the Ku-ring-gai Native Stingless Bee Program educate residents on sustainable beekeeping․ Workshops and training sessions promote stingless bee conservation, fostering public awareness and involvement․
Ku-ring-gai Native Stingless Bee Program
The Ku-ring-gai Native Stingless Bee Program, initiated in 2003, focuses on conserving native bees through education and community involvement․ It provides resources like hives and components, with proceeds funding program activities․ The program emphasizes sustainable beekeeping practices, offering workshops and training to promote the importance of stingless bees in pollination and ecosystem health․ By engaging the community, it aims to protect these vital pollinators and their habitats, ensuring biodiversity for future generations․
Cumberland City Council’s Initiative
Cumberland City Council’s initiative focuses on promoting biodiversity through native stingless bee conservation․ Their “Keepin-A-Hive” program encourages residents to host stingless bee hives, fostering urban pollination․ The council provides educational resources and support, helping households maintain these eco-friendly hives․ This community-driven effort aims to protect local ecosystems while raising awareness about the importance of native pollinators․ By engaging residents, the program contributes to a healthier environment and sustainable future․
Workshops and Training
Workshops and training programs are essential for promoting stingless beekeeping․ These sessions cover hive design, colony management, and best practices for maintaining healthy bees․ Participants learn about constructing artificial hives, pest control, and honey harvesting․ Practical hands-on activities provide valuable experience․ Experts share insights on optimizing hive designs for local climates and species․ Such programs empower individuals to contribute to biodiversity conservation while fostering sustainable beekeeping practices․ They are crucial for spreading knowledge and skills, ensuring the long-term success of stingless bee conservation efforts globally․
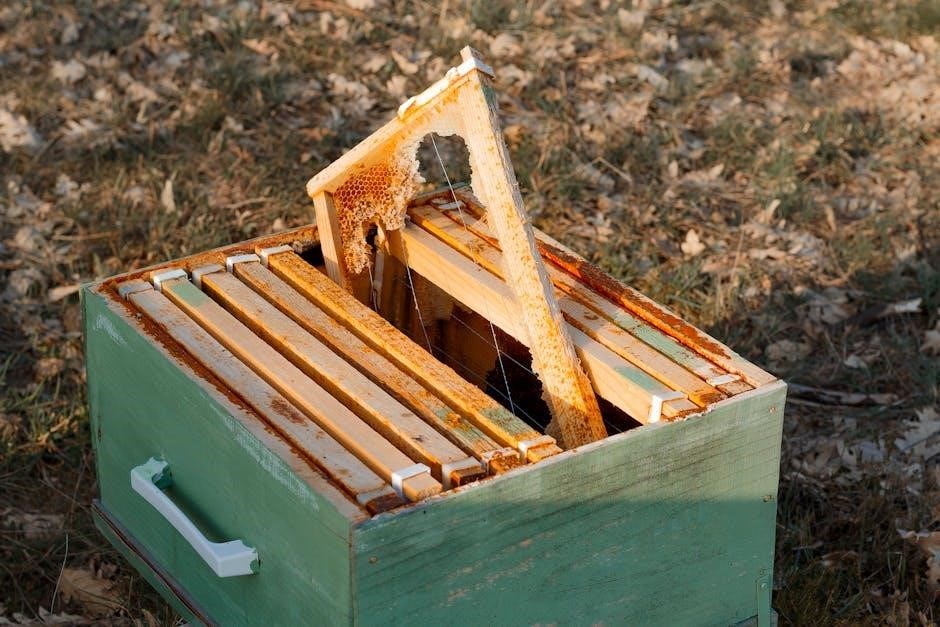

Hive Maintenance and Management
Regular monitoring and inspections ensure hive health․ Controlling pests and diseases is crucial․ Proper honey harvesting techniques preserve colony strength and productivity, ensuring sustainable beekeeping practices․
Monitoring and Inspection
Regular monitoring of stingless bee hives is essential to ensure colony health and productivity․ Inspections help identify issues like pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies early․ Observing bee activity at the hive entrance provides insights into the colony’s strength and overall well-being․ Using tools like observation panels in modern hive designs allows beekeepers to assess hive conditions without disturbing the bees․ Proper inspection techniques minimize stress on the colony, ensuring a thriving environment for honey production and pollination services․ This practice is vital for maintaining sustainable and efficient stingless beekeeping operations․
Pest and Disease Control
Controlling pests and diseases is critical for maintaining healthy stingless bee colonies․ Natural defenses, such as resin use, help entomb invaders like parasitic beetles․ Hive designs, including the ASB dry split box and INPA square modular box, incorporate features to prevent infestations․ Regular inspections and cleaning of hive boxes are essential to detect and eliminate threats early․ Proper ventilation and hygiene practices further reduce disease risks, ensuring the colony remains robust and productive․ These measures are vital for sustainable stingless beekeeping and honey production․
Honey Harvesting Techniques
Honey harvesting from stingless bees requires careful techniques to avoid damaging the colony․ Unlike honeybees, stingless bees produce smaller amounts of honey, stored in propolis-rich pots․ Harvesting involves extracting these pots without harming the brood or workers․ Hive designs, such as the ASB dry split box, incorporate shallow drawers for easy access․ Proper timing and gentle handling are crucial to ensure colony health․ Regular inspections help determine optimal harvest times, balancing productivity with sustainability․ These methods preserve the hive’s integrity while yielding high-quality, unique-tasting honey․

Future Directions in Hive Design
Future hive designs focus on innovative materials like 3D-printed components and modular systems, enhancing sustainability and adaptability to various climates, ensuring optimal bee health and productivity․
Innovative Materials
Modern hive designs incorporate innovative materials like Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PET-G) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), offering durability and climate adaptability․ 3D-printed components enable customized structures, ensuring optimal bee health․ These materials are sustainable, lightweight, and resistant to pests, creating a safe environment for stingless bees․ Their use promotes efficient honey production and ease of maintenance, making them ideal for future hive construction․ Such advancements align with environmental goals, supporting meliponiculture’s growth while reducing ecological impact․
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in hive design include smart sensors and monitoring systems that track temperature, humidity, and pest levels․ These tools enable beekeepers to optimize hive conditions, ensuring colony health․ Advanced materials like 3D-printed components and modular designs improve adaptability and ease of maintenance․ Innovations such as hive monitoring apps and data analytics further enhance management efficiency, promoting sustainable meliponiculture․ These technologies not only improve hive productivity but also contribute to the conservation of stingless bees, making beekeeping more accessible and effective for modern practitioners․

Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability initiatives in stingless bee hive design focus on eco-friendly materials and practices․ Recycled materials, like PET-G and PVC, are increasingly used to construct durable and environmentally conscious hives․ Natural resources such as bamboo and logs are also utilized to minimize environmental impact․ Additionally, community programs promote the use of locally sourced materials, reducing carbon footprints․ These practices not only support biodiversity but also align with global sustainability goals, ensuring the preservation of stingless bees and their habitats for future generations while addressing climate change challenges․
Stingless bee hive design plays a vital role in sustainable agriculture and biodiversity conservation, offering innovative solutions for eco-friendly beekeeping and honey production globally․
Stingless bee hive design is essential for supporting colonies and promoting sustainable agriculture․ Key points include the use of natural and modern materials, climate adaptability, and space efficiency․ These hives enable efficient honey production and pollination services while conserving biodiversity․ Community programs and educational initiatives play a crucial role in popularizing stingless beekeeping․ By focusing on innovative designs and maintenance practices, stingless bee hives contribute significantly to environmental and economic benefits globally․
Final Thoughts on Stingless Bee Hive Design
Stingless bee hive design represents a harmonious blend of tradition and innovation, supporting biodiversity and sustainable agriculture․ By focusing on climate adaptability, space efficiency, and ease of maintenance, these hives promote eco-friendly practices․ Community involvement and educational programs further enhance their adoption, ensuring the preservation of stingless bee populations․ As research and technology advance, future hive designs will likely incorporate even more sustainable materials and cutting-edge features, contributing to global environmental conservation and economic growth․